Have A Tips About How To Handle Exception In Junit
Handling and verifying exceptions in junit 4 in junit 4 there are two primary ways of handling exceptions.
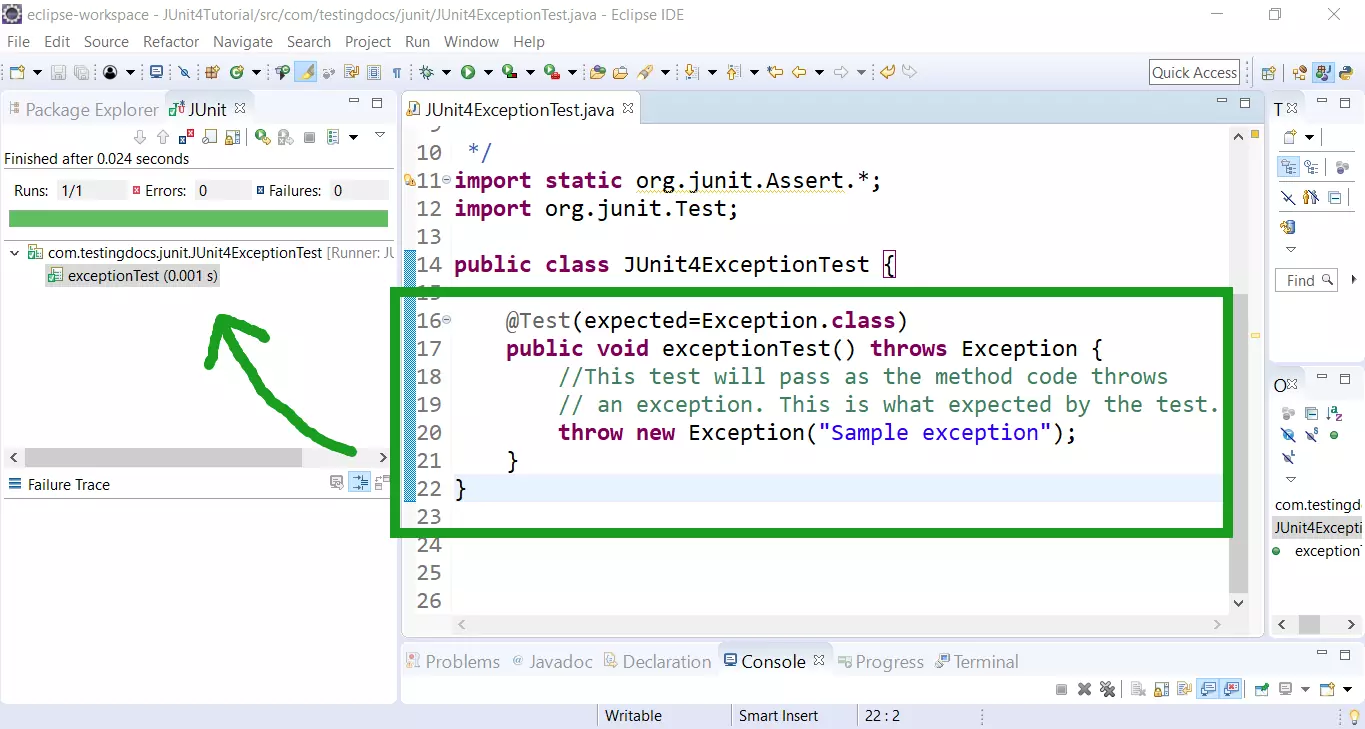
How to handle exception in junit. We will discuss how to test the exception in different versions of junit. In junit there are 3 popular ways of handling exceptions in your test code: The most commonly used method is with the expected field in @test.
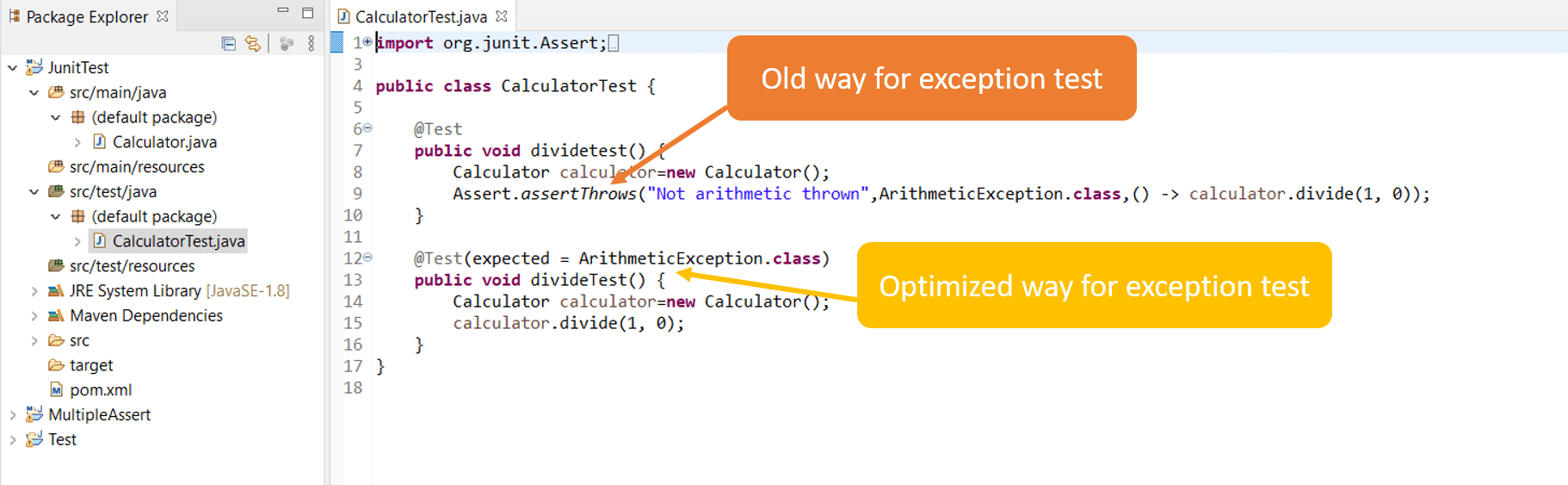
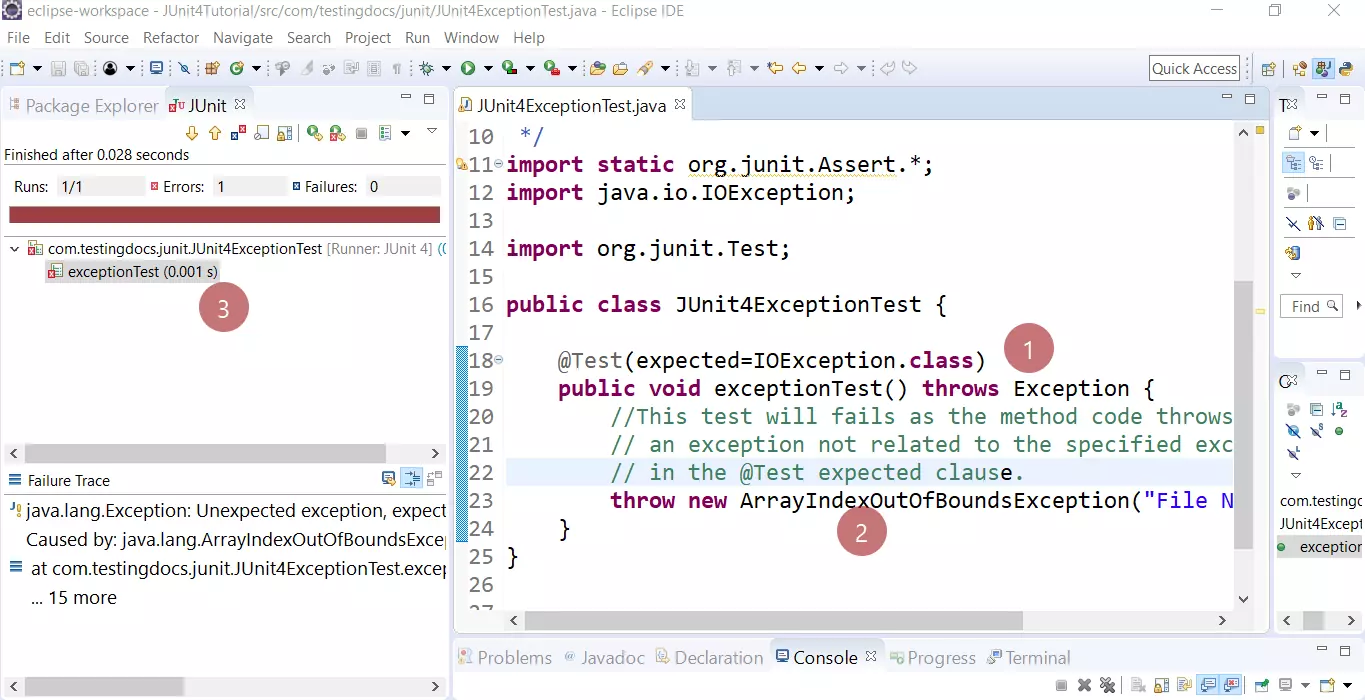
@test ( expected = indexoutofboundsexception. Don’t suppress the exception unless you want the test to pass whether or not the exception is thrown. Junit 5 jupiter assertions api introduces the assertthrows method for asserting exceptions.
Which one should we use and when? Junit provides the facility to trace the exception and also to check whether the code is throwing expected exception or not. In junit there are 3 popular ways of handling exceptions in your test code:
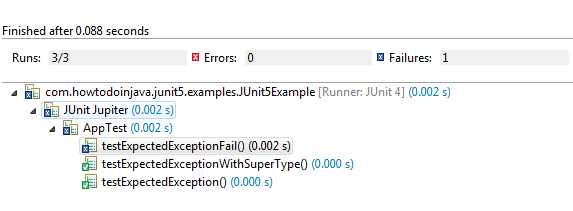
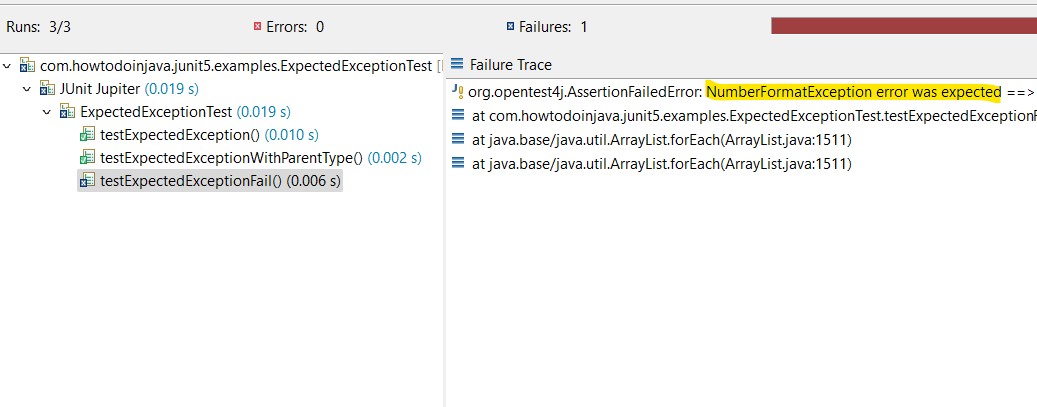
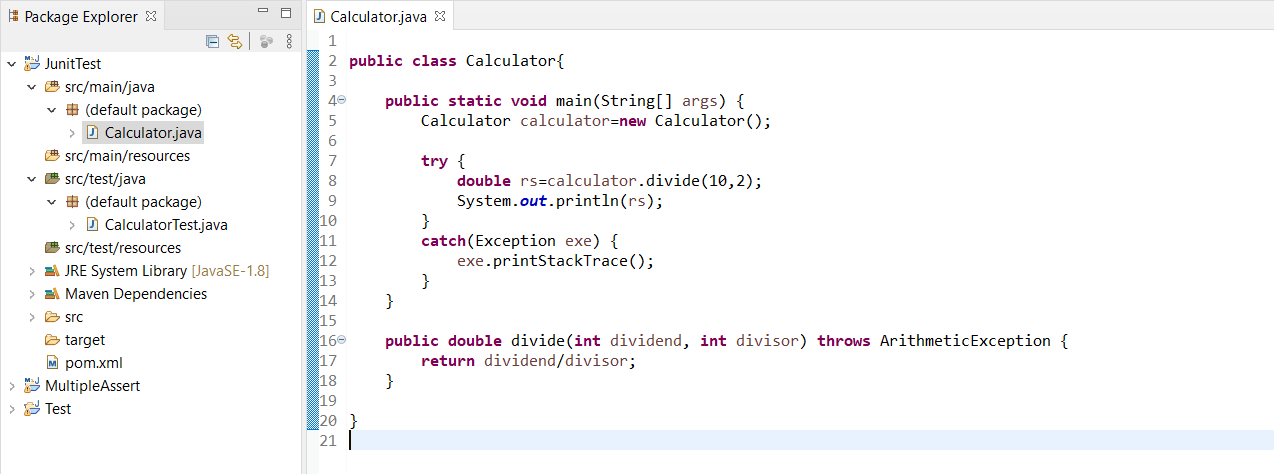
If we wanted to verify that arraylist throws the correct exception, we would write: I followed the documents and wrote the following test case with junit5 but it failed. @test public final void testzero () throws exception { assertequals (zero, service.convert.
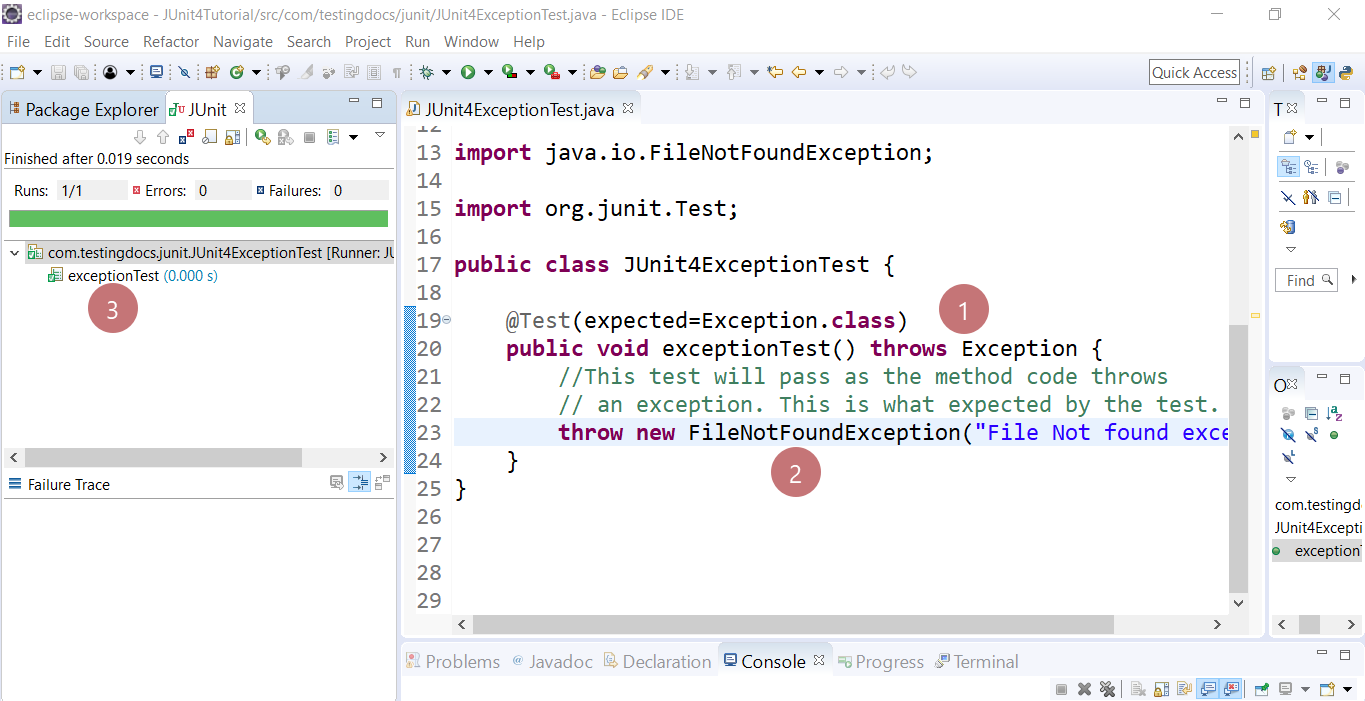
The junit 4 way there’s got to be something in junit that can take care checking the exception type and reporting if it doesn’t match what we expected. (filenotfoundexception) we use the clause. Class) public void empty () { new arraylist ().
You can just let take junit to take care of the exception by adding it to your method. Junit4 provides an easy and readable way for. In junit4 we can use @test (expected = exception.class) and its not possible in junit5.